- Pick up from the Samtech Store in Ambala
To pick up today
Free
- Courier delivery
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
4-5 Days
200+






₹1,500 Original price was: ₹1,500.₹650Current price is: ₹650. (Exc. GST)
To pick up today
Free
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
4-5 Days
200+
The Bernoulli Principle is a fundamental concept in fluid dynamics, which explains the relationship between the speed and pressure of a moving fluid. It is named after the Swiss scientist Daniel Bernoulli, who formulated it in the 18th century.
“As the speed of a fluid increases, its pressure decreases, and vice versa.”
This means that in a steady flow of a fluid (like air or water), where the total energy remains constant, an increase in the fluid’s velocity will lead to a decrease in its pressure, and a decrease in the velocity will lead to an increase in its pressure.
Bernoulli’s equation is usually written as:
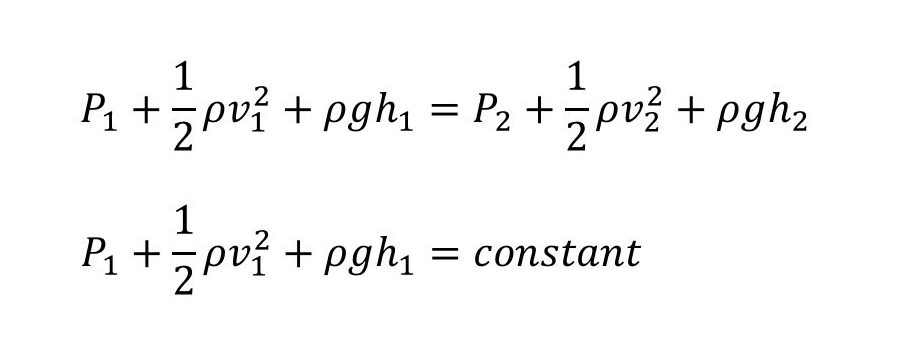
Where:
P = Pressure in the fluid,
ρ = Density of the fluid,
v = Velocity of the fluid,
g = Acceleration due to gravity,
h = Height of the fluid above a reference point.
The equation shows that the sum of three forms of energy in a fluid (pressure energy, kinetic energy, and gravitational potential energy) remains constant if the flow is steady, non-turbulent, and incompressible.
Airplane Wings (Lift):
One of the most common examples of Bernoulli’s Principle in action is the way airplanes generate lift to fly.
Venturi Effect (Carburetor in Engine):
In a carburetor, a narrow section of the pipe (called a venturi) causes air to speed up as it passes through. According to Bernoulli’s principle:
In summary, Bernoulli’s Principle helps explain how air and fluids behave in various situations, from airplane flight to the functioning of everyday objects like pipes and carburetors!
In stock
In stock
In stock
In stock
In stock
No account yet?
Create an Account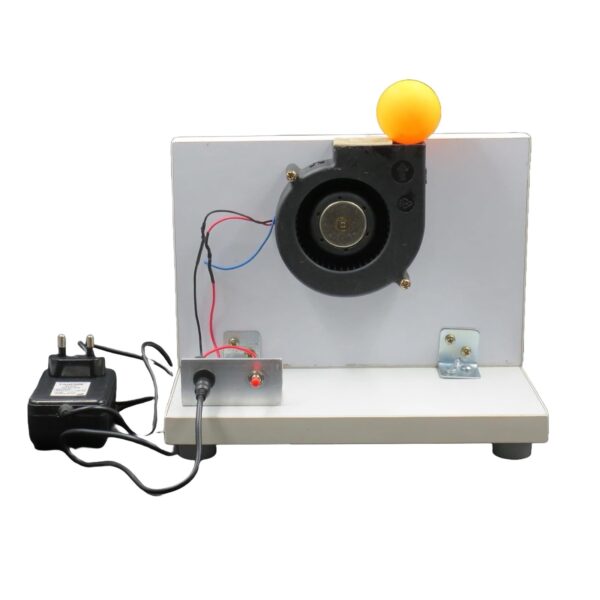
SAMTECH INSTRUMENTS
Typically replies within minutes
Any questions related to Bernoulli Principle Apparatus?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

