- Pick up from the Samtech Store in Ambala
To pick up today
Free
- Courier delivery
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
4-5 Days
200+
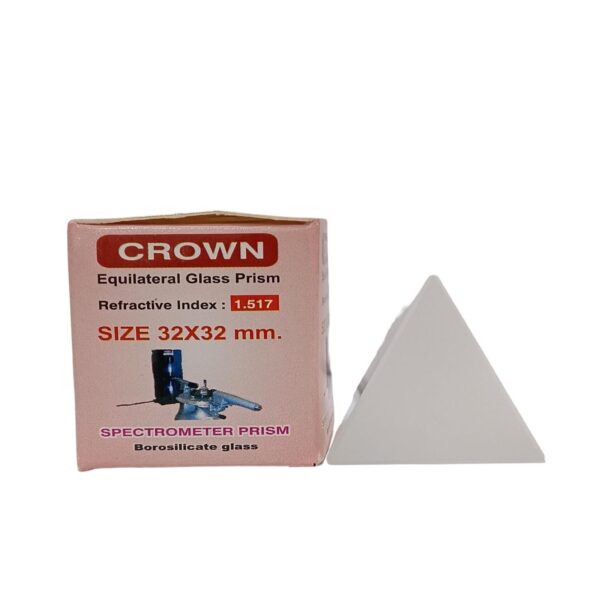





₹500 Original price was: ₹500.₹300Current price is: ₹300. (Exc. GST)
To pick up today
Free
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
4-5 Days
200+
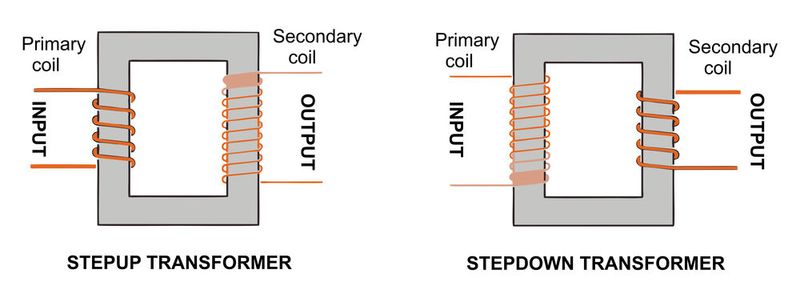
The Step Up Transformer Model that we have developed is an outstanding educational tool that enhances the learning experience for students. This innovative model offers a comprehensive approach to teaching, allowing students to grasp complex concepts more effectively. By engaging with the Step Up Transformer Model, students can deepen their understanding and foster critical thinking skills in a dynamic and interactive environment. This model will significantly contribute to their educational journey and academic success.
In stock
In stock
No account yet?
Create an Account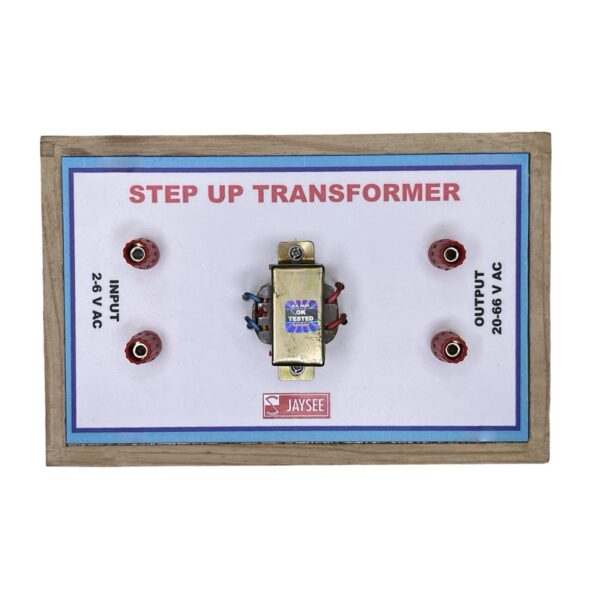
SAMTECH INSTRUMENTS
Typically replies within minutes
Any questions related to Step Up Transformer Model?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

