- Pick up from the Samtech Store in Ambala
To pick up today
Free
- Courier delivery
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
4-5 Days
200+






₹1,000 Original price was: ₹1,000.₹450Current price is: ₹450. (Exc. GST)
To pick up today
Free
Our courier will deliver to the specified address
4-5 Days
200+
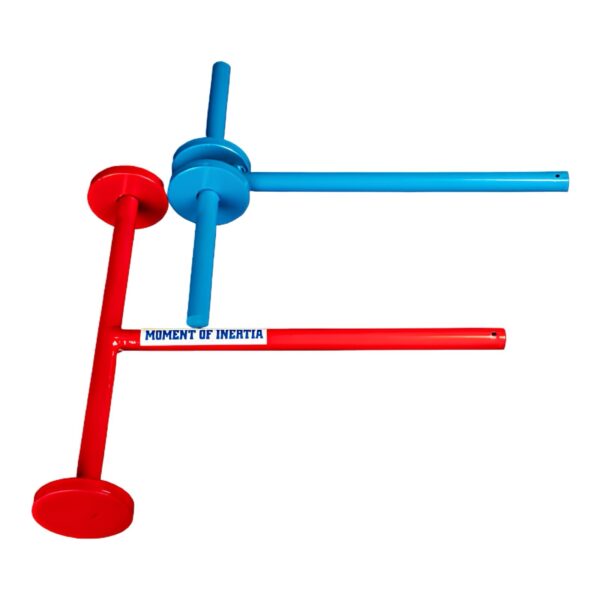
The inertia of motion model illustrates a key principle of physics: an object in motion tends to remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force. This concept is fundamental in understanding how objects interact with each other and their environments. In this model, when a spring is compressed and then released, the stored potential energy in the spring is transformed into kinetic energy, propelling the attached funnel and ball upwards. Both objects initially move together due to the force exerted by the spring, demonstrating their shared momentum at the moment of release.
As the funnel and ball ascend, they exhibit different behaviours governed by inertia. The funnel, affected by air resistance and its mass, eventually reaches a point where it can no longer sustain its upward motion and slows down. It becomes momentarily held back while the ball continues its ascent. This portion of the experiment showcases the concept of inertia; the ball, having started in motion, continues to rise even as the funnel decelerates, illustrating that the forces acting on the two objects differ despite their initial state of motion.
Eventually, the ball’s upward momentum will not last indefinitely. As there are no longer any forces acting on it to propel it upward, it must eventually succumb to gravity and begin its descent. This phase of the experiment highlights the importance of understanding forces in motion—how they interact, the roles they play, and how they lead to observable outcomes. By examining this model, one gains valuable insights into not just inertia but also the fundamental principles that govern motion in our everyday world.
In stock
In stock
In stock
In stock
In stock
No account yet?
Create an Account
SAMTECH INSTRUMENTS
Typically replies within minutes
Any questions related to Inertia of Motion Model?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

